Biotechnology: Powerful Principles, Applications, and Future

Biotechnology: Principles and Applications
Biotechnology is an interdisciplinary field that combines biology, technology, and science, where biological systems, organisms, or derivatives are used to develop new technologies and products. The goal of biotechnology is to understand various aspects of life and apply this knowledge to solve human problems. Research and development in this field have made significant contributions to improving and innovating processes in agriculture, medicine, the environment, and industry.
Principles of Biotechnology
The fundamental principle of biotechnology is the scientific use of organisms and their components. The following key principles are central to biotechnology:
1. Biological Reactions and Modifications
Biological reactions are processes in which biological components such as enzymes, cells, and microorganisms participate. The principle of biotechnology is based on guiding and controlling these reactions. They are widely used in agriculture and medicine, such as in fermentation to produce antibiotics and alcohol, or enzyme-based reactions for diagnostics.
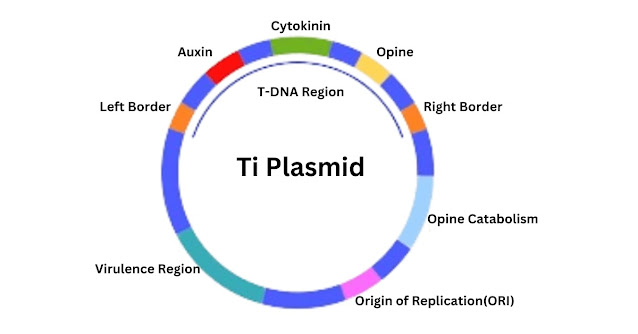
2. Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology)
Gene engineering is the process of altering DNA to bring about changes in the genetic makeup of an organism. This technology is used to achieve specific traits by adding or modifying genes. For example, the development of disease-resistant plants, in which naturally resistant genes are inserted into the plant’s DNA. CRISPR-Cas9, a more recent gene-editing tool, offers precision and efficiency in genome editing, revolutionizing genetic research and therapy.
3. Cell Culture and Tissue Culture
The principle of cell and tissue culture involves growing cells or tissues from organisms under controlled conditions. This technique is widely used in the medical field, such as in organ transplantation, cancer research, and vaccine development, as well as in industrial production like synthetic meat and therapeutic protein synthesis.
4. Microbial Biotechnology
Microorganisms are used in biotechnology to produce biological substances such as antibiotics, vaccines, and other biochemicals. This principle focuses on the controlled large-scale production of microorganisms for industrial use. Engineered microbes are also used for the biosynthesis of complex molecules that are otherwise difficult or expensive to produce.
5. Bioinformatics and Systems Biology
Modern biotechnology also integrates computational tools. Bioinformatics plays a crucial role in analyzing biological data, such as sequencing genomes, protein structures, and modeling biological processes. Systems biology helps understand complex interactions in biological systems, leading to more targeted biotechnological interventions.
Applications of Biotechnology
Biotechnology has diverse applications in various fields of life. Some of the major applications include:
1. Agricultural Biotechnology
Biotechnology has found extensive applications in agriculture. It has led to the development of disease-resistant, pest-resistant, and high-yielding crops. For instance, genetically modified (GM) crops such as Bt cotton and Bt corn, developed using gene engineering techniques, are more resistant to pests and yield higher outputs. Precision agriculture, biofertilizers, and drought-resistant varieties are also emerging innovations.
2. Medical Biotechnology
In the medical field, biotechnology is used in drug production, disease diagnosis, and treatment. Techniques such as gene therapy, antibiotics, vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and biosensors have been developed through biotechnology. For example, the production of insulin, which was once derived from pigs or cows, is now produced using genetically modified E. coli bacteria. Personalized medicine and regenerative medicine are also outcomes of advances in this field.
3. Environmental Biotechnology
Biotechnology has a significant role in environmental conservation. Bioremediation, a biological treatment process, utilizes microorganisms to clean up pollutants from soil, water, and the atmosphere. This technology helps to remove harmful chemicals and contaminants from the environment. Additionally, biofilters, composting, and bioindicators are biotechnological tools used for sustainable environmental management.
4. Industrial Biotechnology
In industrial processes, biotechnology is increasingly used to produce high-quality biological products on a large scale. Enzymes, biofuels, biodegradable plastics (bioplastics), and biopolymers are examples of products that are made possible through industrial biotechnology. It promotes cleaner, more sustainable manufacturing processes.
5. Food and Nutrition
Biotechnology also plays an important role in the food industry. It is used to improve the quality of food, develop food preservatives, and produce protein-rich food products. For example, probiotic yogurt, which contains beneficial bacteria for health, is a product of biotechnology. Golden rice, enriched with vitamin A, is another example aimed at combating malnutrition.
6. Marine Biotechnology
An emerging field, marine biotechnology, utilizes resources from oceans and marine organisms to develop products in health, cosmetics, and food. Algae are now used to produce biofuels, food supplements (like omega-3), and biodegradable packaging.
Future Prospects and Ethical Considerations
Biotechnology is poised to play an even greater role in the future, particularly with advances in synthetic biology, stem cell research, artificial organs, and nanobiotechnology. These innovations promise to transform medicine, agriculture, and energy, making processes more efficient and personalized.
However, with these advancements come ethical and social considerations. Issues such as:
- Genetic privacy and discrimination
- Biopiracy and intellectual property
- Environmental risks of GMOs
- Animal rights and experimentation
- Accessibility and affordability of biotech treatments
must be addressed through proper regulation, public awareness, and global cooperation.
Conclusion
The field of biotechnology serves as a strong bridge between science and technology. Its principles and applications have not only revolutionized industries and medicine but have also impacted every aspect of society. From producing life-saving medicines to enhancing food security and environmental health, biotechnology is a powerful tool in addressing global challenges. However, along with its development, it is crucial to consider aspects of biosafety, ethics, and environmental impacts to ensure that the benefits of biotechnology are maximized while minimizing its risks.







2 thoughts on “Biotechnology: Powerful Principles, Applications, and Future”